Deep Breathing Exercises to Reduce Anxiety

Anxiety disorders and panic attacks affect millions of people’s mental health worldwide. The symptoms of anxiety can range from mild to severe and can impact a person’s ability to function in their daily life.
Deep breathing exercises are a simple yet effective way to reduce anxiety symptoms and benefit your mental health and well-being. In this article, we will explore how deep breathing exercises can help calm the nervous system and provide relief from stress and anxiety.
How Shallow Breathing Contributes to Anxiety
Shallow breathing or upper chest breathing is a common pattern of breathing that is often associated with anxiety. When we take shallow breaths, we do not take in enough oxygen, and this can cause an increase in heart rate, blood pressure, and tension in the body. Breathing patterns like this can become a habit without even realizing it.
Shallow breathing activates the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. This causes a stress response which leads to a feeling of anxiety. Rapid breaths have the same effect. They trigger the same nervous system response that can cause you to feel anxious.
How Breathing Exercises Can Help Calm Your Nervous System
Breathing exercises can help to calm the nervous system, promote relaxation, and provide anxiety relief. Deep breathing and slow breathing techniques can activate the vagus nerve and the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “rest and digest” response. Breathing properly and learning breath control can help to lower blood pressure, reduce tension in the body, and decrease feelings of stress and anxiety.
Studies have shown that mindfulness based stress reduction techniques, like conscious breathing exercises, may be as effective as medication in reducing anxiety and depression.
Deep Breathing
Deep breathing, also known as abdominal breathing, involves taking a slow, deep breath from the belly, allowing the lungs to fully expand. This technique can be done sitting or lying down, and it is a simple way to promote relaxation and calmness.
Deep breathing exercises can also be helpful for disorders like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The symptoms of COPD include breathing more shallowly and shortness of breath. Breathing exercises can help COPD patients better manage their symptoms by strengthening the diaphragm muscle, which helps to open the lungs fully.
Slow Breathing
Slow controlled breathing involves taking slow easy breaths in through the nose and out through the mouth, slowing breathing down to a rate much slower than your normal rate. This technique can help to regulate breathing, increase breath awareness (also called coherent breathing), reduce feelings of stress and anxiety, and trigger a relaxation response.
Simple Breathing Exercises
There are many breathing exercises that are easy to incorporate into your everyday life and can help you to feel calm. You can try each of these relaxation techniques to see which works best for you.
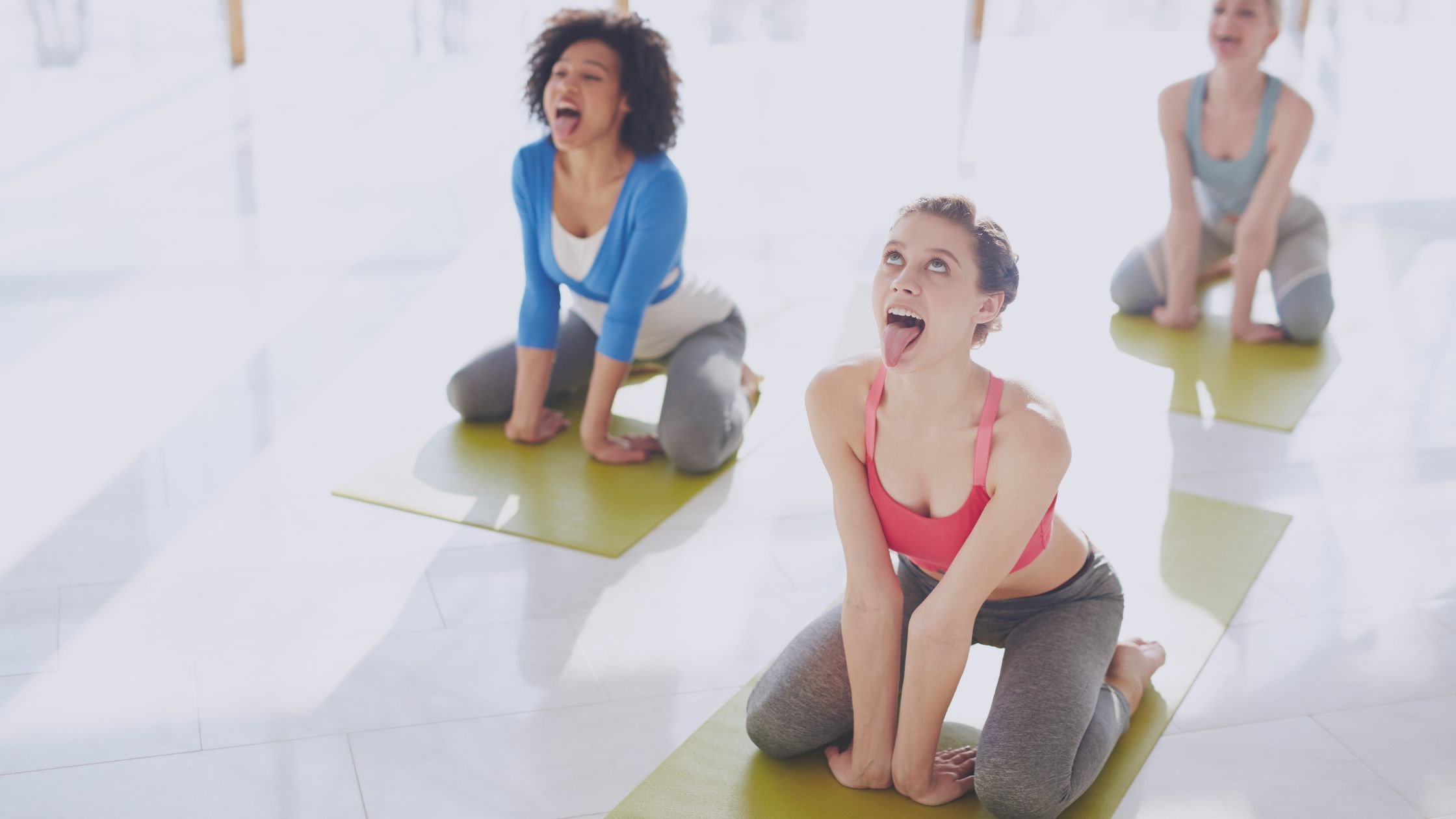
Lion’s Breath
Lion’s Breath is a powerful breathing exercise that can help to release muscle tension in the body.
To do this exercise, sit in a comfortable position, keep your shoulders relaxed, inhale slowly through the nose, and then exhale forcefully through the mouth while sticking out your tongue and making a “ha” sound as you exhale completely.
For full details on this technique read the post Simha Pranayama: Master Lion’s Breath to Release Tension Now!

Belly Breathing or Diaphragmatic Breathing
Belly breathing, also known as diaphragmatic breathing, involves taking slow, deep breaths correctly using the stomach muscles to breathe more efficiently. This technique can help to promote relaxation and calmness.
To do this exercise, you can start by lying down with either a book or your hand on your abdomen to help you feel the movement of your breath. Take a deep relaxing breath in slowly through your nose, fill up your belly letting your stomach rise. Then completely exhale through your mouth allowing your belly to fall.
Repeat the process for a few additional minutes until your body feels relaxed.
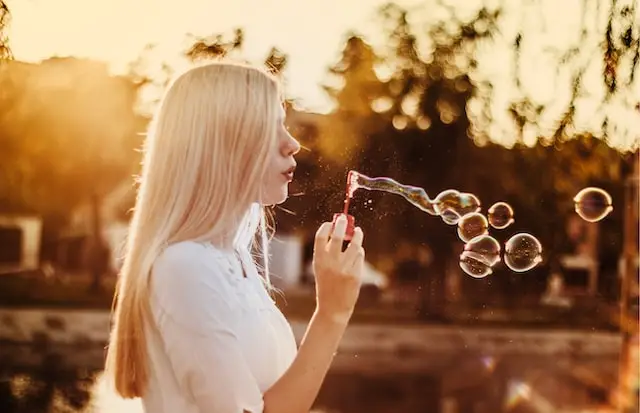
Pursed Lips Breathing
Pursed lips breathing is a simple breathing technique that can help to regulate breathing and reduce feelings of anxiety.
To do this exercise, keep your jaw relaxed while inhaling deeply through the nose, then exhale slowly through pursed lips, as if you are blowing out a candle or blowing a bubble.
Humming Bee Breath
Humming bee breath or Bhramari Pranayama, is a technique that can help to promote relaxation and calmness by stimulating the vagus nerve. This type of breathing helps to relax the body and mind, which can be very helpful for those suffering from anxiety.
To do this exercise, breathe deeply in through the nose, then allow your breath to leave your body slowly while making a soft humming sound sound.
For full details on this technique read the post Humming Bee Breath: A New Way to Reduce Anxiety Naturally!
Alternate Nostril Breathing
Alternate nostril breathing is a technique that can help to balance the body’s energy and promote relaxation, calm the body, and improve circulation. It is also thought to stimulate the pituitary gland, which controls many important physiological processes like growth and development, metabolism, the production of hormones, and the body’s response to stress.
To do this exercise, sit in a comfortable position, then fold over your middle fingers allowing you to use your right thumb to close your right nostril and inhale quietly through the left nostril. Then, use your right ring finger to close your left nostril and gently breathe out through the right nostril. Repeat the process, alternating nostrils and keeping your mouth closed.

Box Breathing Exercise
Box breathing is a technique used to promote relaxation. Box breathing creates a calming focus with an easy-to-follow breathing pattern. It can be used during meditation or whenever you feel stressed.
To do this exercise, inhale slowly through the nose for four counts, hold for two counts, then exhale through the mouth for four counts. Repeat the process three times.
4-7-8 Breathing Exercise
4-7-8 breathing is a technique often used to reduce stress and help with insomnia and trouble staying asleep. It may also be used as part of a relaxation exercise before going to work or other stressful situations. The 4-7-8 breathing technique is easy to do, and you can do it anywhere.
To do this exercise, take a deep breath in through the nose for the count of four, hold your breath for seven counts, then exhale through the mouth for eight counts. Repeat this process three times.
For full details on this technique read the post 4-7-8 Breathing for Better Sleep – How To Do It Right!
Practice Matters
Breathing exercises take practice, so don’t worry if you don’t get it right the first time. Keep practicing, and with time, you’ll become more comfortable with controlled breathing techniques.
It’s also important to note that while breathing exercises can help alleviate anxiety, it’s always best to consult with a mental health professional if you’re experiencing severe anxiety disorder or panic attacks.
Start Your Own Practice
Breathing exercises are an effective way to reduce stress and anxiety. By practicing coherent breathing, diaphragmatic breathing, and other breathing techniques, you can activate your parasympathetic nervous system, which can help calm your mind and body. Remember, practice makes perfect, so keep at it and enjoy the benefits of mindful breathing.
If you’d like to learn more about how pranayama, yoga breathing, and breathwork exercises affect your nervous system and the types of exercises check out my blog post How Breathwork Works? Effective Practice or Just Woo Woo.














